Mobile payments have become increasingly popular in recent years, allowing users to make purchases quickly and securely using their mobile devices. Two of the most widely used mobile payment services are Apple Pay and Google Pay. But which one offers better security for your payments? This article examines the security features of Apple Pay and Google Pay to help you determine which service may be better for your needs.
How Apple Pay Works
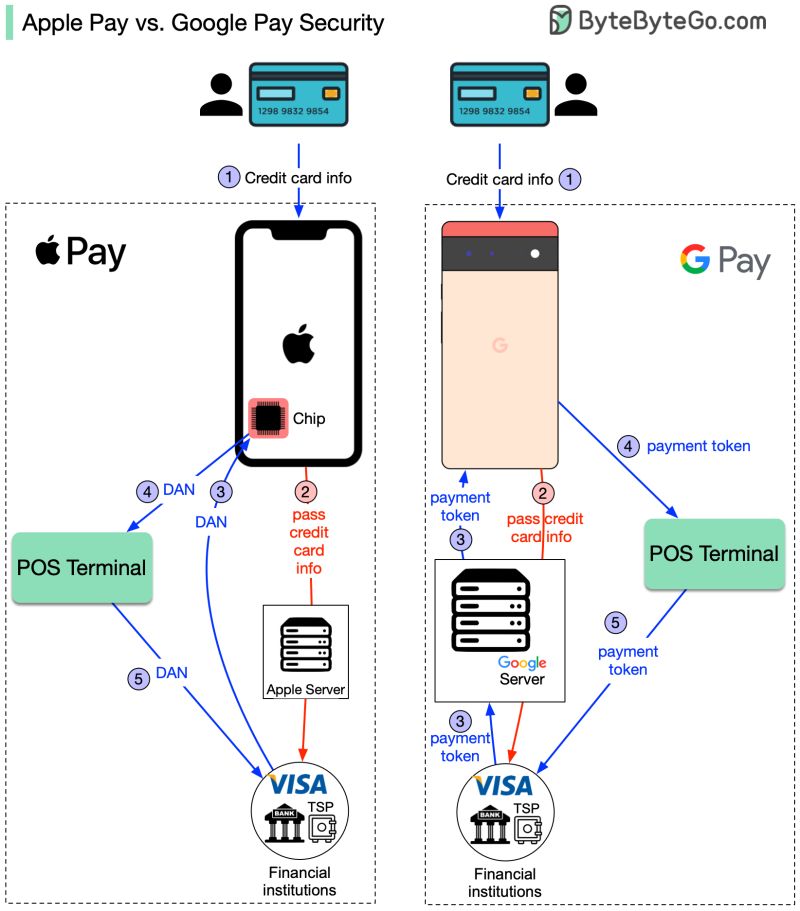
Apple Pay allows users to store their credit and debit cards on their iPhone or Apple Watch and use them to make payments in stores, apps, and on the web. Here’s an overview of how Apple Pay works:
- To set up Apple Pay, users add their card information to the Wallet app on their iPhone or iPad. This can be done by entering card details manually or using your iPhone’s camera to scan your card.
- The actual card numbers are not stored on your device or on Apple’s servers. Instead, a unique Device Account Number is assigned and encrypted and securely stored in your device’s Secure Element, a dedicated chip designed to store payment information safely.
- When you make a payment using Apple Pay, your iPhone or Apple Watch communicates wirelessly with the point of sale terminal using Near Field Communication (NFC) technology.
- Your Device Account Number, along with a transaction-specific dynamic security code, are sent to the merchant’s terminal. Your actual credit or debit card number is never shared.
- The merchant then contacts your bank or card issuer to process and authorize the payment. Once approved, your payment is complete.
Apple Pay Security Features
Apple Pay employs a range of features focused on maintaining the security of your payments and payment information:
- Secure Element: The Device Account Numbers and other sensitive payment data are stored in the Secure Element, an encrypted chip separate from the rest of the phone’s operating system and data. This helps isolate payment info from malware or viruses.
- Tokenization: Your actual card number is replaced with a unique Device Account Number, or token, during each transaction, so your real card number is never shared or transmitted.
- Dynamic security code: A one-time, unique security code is generated with each purchase, adding an extra layer of security.
- Biometric authentication: Apple Pay transactions on iPhone or Apple Watch must be authorized using Face ID, Touch ID, or passcode, providing convenience while ensuring only you can approve payments.
- Network security: Each transaction is encrypted and allowed to pass through a dedicated, encrypted network before reaching your bank or card issuer for verification.
- Wallet specifics: Credit and debit cards added to Apple Wallet can only be used to make payments. The Wallet app does not store other sensitive information like bank accounts, statements, or personally identifying information beyond basic card info.
How Google Pay Works
Formerly known as Android Pay, Google Pay allows Android smartphones and Wear OS smartwatch users to make mobile payments quickly and conveniently. Here’s an overview:
- To set up Google Pay, users add their credit or debit card details through the Google Pay app or website. Card details are stored in the cloud.
- When making a payment, your phone communicates with the payment terminal via NFC. A virtual account number representing your card is sent, along with a one-time security code, to process the transaction.
- Your actual card number is not shared with the merchant. Google Pay doesn’t even share your name or other personal info – just the virtual card number.
- Your bank or card issuer receives the request and verifies the security code before approving the payment.
- You then receive a notification that your payment succeeded on your phone. For in-store payments, a receipt is also usually sent to your email.
Google Pay Security Features
Google employs multiple security layers to help keep payments safe:
- Tokenization: As with Apple Pay, your actual card number is replaced by a unique virtual account number during each transaction.
- Virtual account numbers: These tokens represent your card but can’t be leveraged for fraud outside the tokenized Google Pay transaction.
- Dynamic security code: This unique one-time code is generated for each purchase, adding an extra layer of security.
- Payment tokens: Tokens are stored in a secure Google cloud environment instead of directly on your device. If your phone is lost or stolen, your payment info remains protected.
- Data encryption: All data transmitted during transactions is encrypted for security.
- Biometric authentication: For phones with fingerprint sensors or face recognition, payments must be authorized biometrically before being sent.
- Google 2SV: Users can enable two-step verification for an extra layer of account security beyond biometric authentication.
- Card specifics only: The Google Pay app only has access to basic card information needed for payments. It does not access other sensitive financial data.
Apple Pay vs Google Pay: Which is More Secure?
So which mobile payment service offers better security – Apple Pay or Google Pay? Here is a comparison of some key security factors:
- Device storage: Apple Pay stores payment tokens and data securely on the device’s encrypted Secure Element. Google Pay stores data in the cloud, with payment tokens stored on Google servers.
- Tokenization: Both services rely on tokenization to avoid exposing real card numbers during transactions. This prevents fraud and protects card data.
- Biometric authentication: Apple Pay uses Face ID or Touch ID. Google Pay offers fingerprint or face unlock where available. Both require biometric or passcode authorization for each payment.
- Dynamic codes: Both Apple Pay and Google Pay generate a dynamic security code with each transaction for an added layer of security.
- Encryption: Both services employ end-to-end encryption for all payment data in transit between devices, merchants, and banks.
- Wallet access: Apple Wallet only accesses minimal card information needed for payments. The Google Pay app also has limited access to sensitive financial data, reducing exposure.
- Support: Apple devices tend to get software updates for longer than Android phones, ensuring continued support for Apple Pay security.
Overall, experts regard Apple Pay and Google Pay as very secure forms of mobile payment. Both leverage similar security technologies like tokenization, biometric authentication, encryption, and dynamic codes to protect payments.
Apple Pay has an advantage for storing sensitive data in a dedicated Secure Element chip with additional hardware encryption. Google Pay relies more on software encryption and cloud storage instead.
But both are widely accepted as far more secure than using physical credit cards, thanks to unique transaction codes and the elimination of card numbers from the transaction process. Your financial data also never touches retailer systems, offering protection against merchant data breaches.
Neither system is inherently more hackable or vulnerable than the other based on public information – both appear very well engineered for security. So you can consider digital wallet selection based more on smartphone OS preference or other desired features versus strictly security. Proper usage also remains important – make sure to use strong passcodes/biometrics and do not jailbreak or root phones. As mobile payments become more common, Apple Pay and Google Pay both remain excellent choices with strong safety assurances.
Key Takeaways on Apple Pay vs Google Pay Security
- Both Apple Pay and Google Pay leverage tokenization, encryption, biometrics, and dynamic codes to securely process payments without exposing real card numbers.
- Apple Pay stores payment data securely on a dedicated chip with hardware encryption, while Google Pay relies on software encryption and cloud storage.
- Experts regard both services as very secure, far more than physical cards, thanks to unique per-transaction tokens and encryption.
- Neither Apple Pay or Google Pay can be regarded as significantly more hackable or vulnerable based on current knowledge – both utilize industry best practices.
- Hardware encryption gives Apple Pay a slight edge, but both are excellent choices. Use proper security practices for strong protection regardless of which service you choose.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both Apple Pay and Google Pay are regarded as highly secure forms of mobile payment that utilize industry-leading security practices like encryption, tokenization and biometric authentication. Apple Pay benefits slightly from additional hardware-based encryption, while Google Pay offers the flexibility of cloud storage. Overall experts regard both services as excellent choices that are far more secure than paying with a physical card. Whichever mobile wallet you choose, be sure to use proper security practices like using strong passcodes and not jailbreaking your device to ensure your payments remain protected. Both services allow you to take advantage of the speed and convenience of mobile payments while enabling transactions that are authorized and processed securely.
FAQ on Apple Pay vs Google Pay Security
Here are answers to 20 frequently asked questions comparing the security of Apple Pay vs Google Pay:
- Is Apple Pay or Google Pay more secure?
Experts regard Apple Pay and Google Pay as equally secure overall. Both leverage similar encryption, tokenization, biometrics, and dynamic codes to protect transactions. Apple Pay has an advantage with dedicated hardware encryption, while Google Pay offers cloud storage flexibility. But there is no clear winner – both far surpass physical card security.
- Does Apple Pay store my actual credit card number?
No. Apple Pay utilizes device-specific tokens so your actual card numbers are never stored on your device or shared during transactions.
- Does Google Pay store my real card number?
No. Like Apple Pay, Google Pay uses virtual account numbers/tokens so your real card data is never exposed or stored in the app.
- Is Apple Pay safe to use?
Yes, Apple Pay is regarded by experts as extremely safe to use thanks to hardware encryption, biometric authentication, and other security features that protect your payment info.
- Is Google Pay safe for payments?
Yes, Google Pay uses virtual account numbers, software encryption, and other protections like biometric authentication to securely process transactions without exposing your financial data.
- Can my iPhone be hacked to steal Apple Pay data?
It is highly unlikely given Apple Pay’s hardware-based encryption isolated from the rest of iOS. As long as you avoid jailbreaking your phone, your payment info remains securely stored.
- Can someone hack my Android phone and access Google Pay?
It’s very unlikely given Google Pay’s security protections. As long as you don’t root your device and keep your phone secure, your payment info stays protected.
- Is one more secure than the other for in-store payments?
No, experts consider Apple Pay and Google Pay equally secure for in-person payments using NFC terminals. Both transmit tokenized data and dynamic codes without your actual card number.
- Which has the best security for online payments?
Apple Pay and Google Pay offer similar security for online payments via encrypted digital wallets. Both keep your real card number hidden from merchants. Overall, they offer comparable security.
- Do I need an internet connection to use Apple Pay or Google Pay?
You need an internet connection for the initial wallet setup, but both services can process transactions offline using tokenized data and generate security codes. An internet connection is preferred but not required.
- Are payments immediately processed with Apple/Google Pay?
Transactions are processed in seconds, faster than chip/PIN payments. Payment tokens and codes are transmitted directly to banks for real-time authorization and settlement.
- Can someone steal my phone and make purchases with my cards?
No. Both services require biometric authentication (Face ID, fingerprint, etc) or passcode entry to authorize each transaction, even with stolen devices. Your payment cards stay protected.
- Are jailbroken or rooted phones less secure?
Yes, compromising iOS or Android security reduces protections for any sensitive data, including Apple/Google Pay info. Avoid jailbreaking or rooting phones for maximum security.
- Is device encryption needed for Apple/Google Pay security?
Device encryption provides an extra layer of security, but tokenized data stays protected regardless for both services. Encryption is still recommended as a best practice when available.
- Do retailers or merchants see my actual card data?
No, your real card number and other personal info is never shared with merchants or retailers when using Apple Pay or Google Pay. They only receive tokenized data specific to that transaction.
- Can tokenization be hacked to steal card data?
No, security experts regard tokenization as very secure. The virtual account numbers cannot be reverse-engineered or used outside the tokenized transactions to steal real payment card details.
- Are dynamic security codes foolproof?
Dynamic codes provide an important extra layer of security that protects against cloning or reuse. However, no single measure is completely foolproof on its own. Modern payment services combine multiple measures for robust protection.
- If my physical card gets stolen, is Apple/Google Pay affected?
No, since Apple Pay and Google Pay don’t transmit your actual card number, your mobile payments remain secure and unaffected even if your physical card is lost or stolen. Just replace/cancel the physical card.
- Do I need a bank app to use Apple/Google Pay?
No, you can securely add cards directly through the Apple Wallet or Google Pay app. Bank apps may offer convenience but are not required to store or use cards with either service.
- Is one app more convenient than the other for payments?
Apple Pay and Google Pay offer similar convenience, allowing quick tap-and-pay mobile transactions that are faster and simpler than using physical cards. Either service provides smooth, hassle-free payment experiences.
Conclusion
In summary, while nuances exist, Apple Pay and Google Pay both provide excellent security for mobile payments via rigorous encryption, intelligent tokenization, biometrics, and transaction-specific dynamic codes that keep your card details private. This allows you to enjoy the speed and simplicity of mobile wallets while remaining well-protected against potential threats. As long as you take care to avoid compromising your device’s security via jailbreaking or rooting, you can confidently use either Apple Pay or Google Pay knowing your financial data stays safe from hackers and vulnerabilities.
.